Potential Drawbacks and Considerations
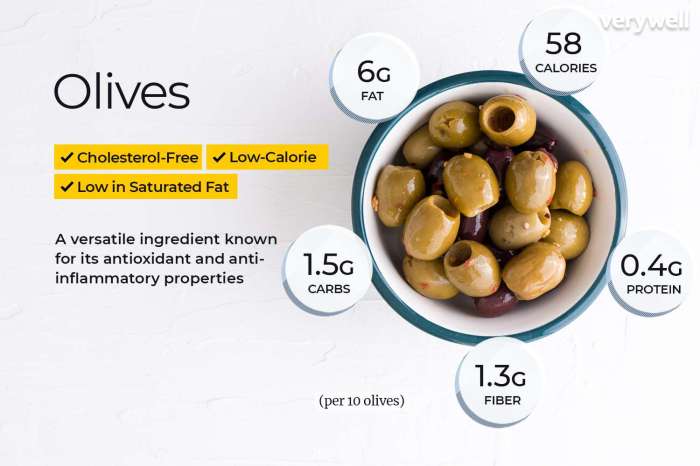
Nutrition facts for black olives – While black olives offer a range of nutritional benefits, it’s crucial to acknowledge potential downsides associated with their consumption, particularly when consumed in excess. Understanding these drawbacks allows for informed and balanced enjoyment of this flavorful fruit.The primary concern with black olive consumption revolves around their sodium content. Black olives, especially those that are processed and preserved, are naturally high in sodium.
A comparative analysis of the nutritional profiles of various foods reveals interesting discrepancies. Black olives, for instance, offer a significant source of monounsaturated fats and dietary fiber. However, a contrasting example can be found by examining the nutritional composition of breakfast cereals such as those detailed in the nutrition facts apple jacks data, which often highlight a higher sugar content.
Returning to black olives, their nutritional value should be considered within a balanced dietary context.
Excessive sodium intake is linked to various health problems, including hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and fluid retention. Therefore, individuals with pre-existing conditions such as hypertension or heart disease need to be particularly mindful of their black olive consumption.
Sodium Content and Health Implications
The high sodium content in black olives is a significant factor to consider. A typical serving of black olives can contribute a substantial portion of the recommended daily sodium intake. For example, a 100g serving of canned black olives can contain upwards of 500mg of sodium, depending on the brand and processing method. This highlights the need for moderation, especially for individuals sensitive to sodium.
Regular monitoring of sodium intake through dietary tracking apps or consultation with a registered dietitian can aid in managing sodium levels effectively. Reducing sodium intake can contribute to better cardiovascular health and blood pressure management.
Interactions with Medications and Health Conditions
While not extensively documented, the high sodium content in black olives could potentially exacerbate conditions like hypertension or interact with certain medications designed to manage blood pressure or fluid balance. Individuals taking diuretics or other medications affecting sodium levels should consult their physician or pharmacist regarding the appropriate consumption of black olives to avoid potential adverse effects. Specific interactions would depend on the individual’s health status and the medications they are taking.
Processing and Preservation Methods
The processing and preservation methods used for black olives can also impact their nutritional profile and potential drawbacks. Many commercially available black olives undergo a process involving brining, which contributes significantly to their sodium content. Furthermore, some processing methods might involve the addition of preservatives or other additives, which may be of concern to some individuals. Choosing olives packed in water or oil, rather than brine, can help reduce sodium intake.
Opting for organic, minimally processed black olives might minimize exposure to potential additives.
Potential Downsides and Precautionary Measures, Nutrition facts for black olives
The following points summarize potential downsides and recommended precautionary measures when consuming black olives:
- High Sodium Content: Limit consumption, especially for individuals with hypertension or heart conditions.
- Potential Medication Interactions: Consult your doctor or pharmacist if you are on medication that affects sodium levels or blood pressure.
- Additives and Preservatives: Choose minimally processed or organic olives to minimize exposure to additives.
- Moderation is Key: Enjoy black olives as part of a balanced diet, rather than consuming large quantities.
- Read Food Labels Carefully: Pay attention to sodium content per serving.
Visual Representation of Nutritional Information: Nutrition Facts For Black Olives

A compelling visual representation of nutritional data can significantly enhance understanding and engagement. Effectively showcasing the nutritional profile of black olives requires a multi-faceted approach, combining imagery with data visualization. This allows for a richer, more intuitive grasp of the olive’s nutritional value.
Black olives, visually, are typically depicted as plump, oval-shaped fruits with a deeply wrinkled surface. Their size varies, ranging from approximately 1 to 2 inches in length, depending on the variety and growing conditions. The color is a deep, inky black, sometimes with purplish hues. The texture is firm yet yielding, suggesting a moist interior. A high-quality image would capture the subtle variations in shading and the glistening sheen often present on the surface of a ripe black olive.
The overall impression should convey both richness and a satisfying textural complexity.
Comparison of Nutritional Content in Olives
A bar graph or pie chart effectively compares the nutritional content of black olives with other common table olives, such as green olives and Castelvetrano olives. The graph would present data on key nutrients per serving size (e.g., 100g). The data points to be included would be: total fat, monounsaturated fat, polyunsaturated fat, saturated fat, sodium, fiber, vitamin E, and potentially other significant micronutrients.
For example, a bar graph would display separate bars for each olive type, with the height of each bar representing the quantity of a specific nutrient. A legend would clearly identify each olive type and the nutrient being measured. A pie chart could similarly represent the proportion of different macronutrients (fat, carbohydrates, protein) within each olive type, giving a clear visual comparison of their overall nutritional composition.
This visual comparison would highlight the differences and similarities in nutritional profiles among different olive varieties, allowing for informed choices based on individual dietary needs and preferences.
Question Bank
Are black olives high in sodium?
Yes, black olives, particularly those that are processed, can be relatively high in sodium. Individuals with sodium-restricted diets should consume them in moderation.
Can I eat black olives if I have high blood pressure?
While black olives contain beneficial compounds, their sodium content may negatively impact blood pressure. Consult your physician regarding appropriate consumption levels.
How are black olives processed?
Black olives undergo a process of curing and fermentation, which involves lye treatment and brine soaking to develop their characteristic flavor and texture. Different processing methods may affect the final nutrient content.
Are black olives a good source of fiber?
Yes, black olives provide a moderate amount of dietary fiber, contributing to digestive health.
